

In today’s electronics industry, efficient thermal management is critical for high-performance devices. Skiving heat sink technology has emerged as one of the most effective solutions for dissipating heat in compact and high-power applications. Whether it’s for CPUs, power modules, LEDs, or industrial electronics, a skived fin heat sink ensures that components operate reliably under heavy loads.
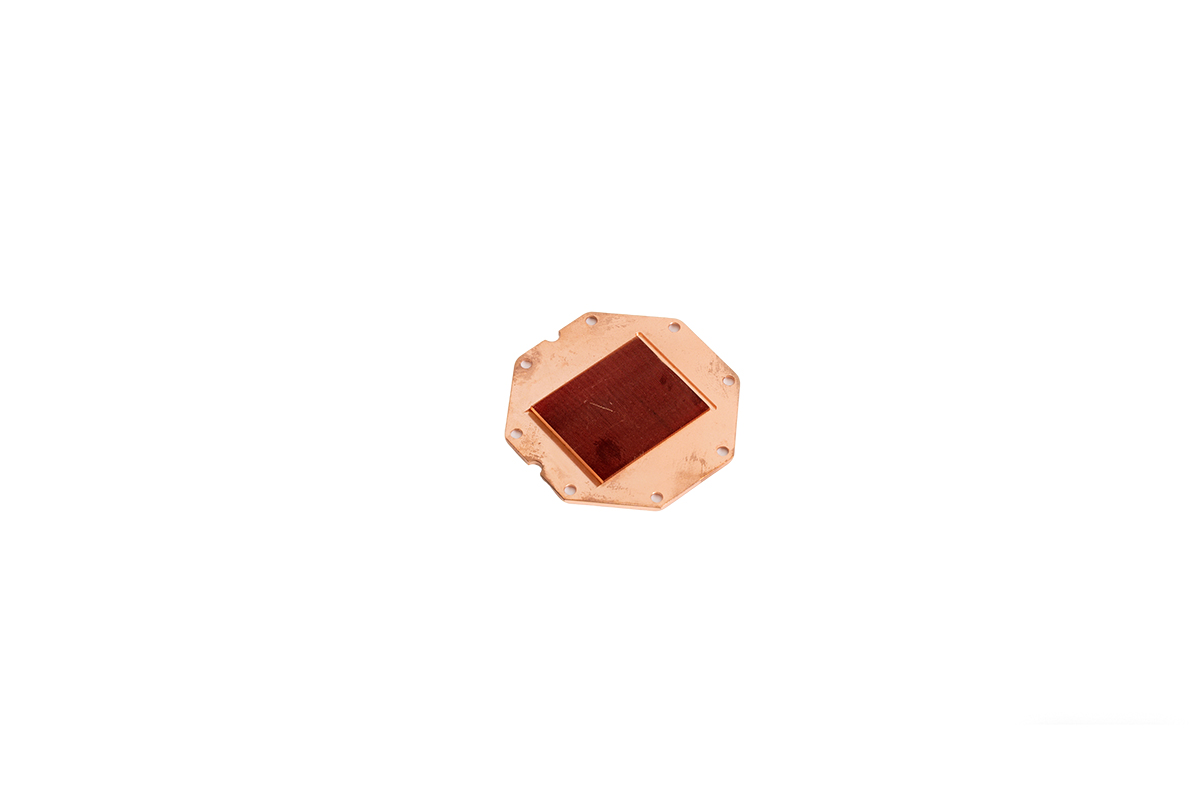

A skiving heat sink is a type of heat sink manufactured using the skiving process, where thin fins are sliced directly from a solid metal block. This process allows for extremely high fin density, creating a large surface area that facilitates rapid heat dissipation.
Key features include:
High thermal efficiency with skived fin design
Compact footprint for tight electronic layouts
Superior mechanical strength due to integrated fin-base construction
Compatibility with heatsink fan systems for active cooling
A skived copper heatsink leverages the high thermal conductivity of copper, making it ideal for applications with demanding heat loads. The copper skiving process allows precise control of fin thickness and spacing, enabling custom designs tailored to specific devices.
Skiving heat sinks are typically made from high-quality metals to maximize heat transfer:
Copper: Produces skived copper heatsink with excellent thermal conductivity. Copper skiving allows thin, high-density fins that quickly transfer heat from the base to the fins.
Aluminum: Lightweight and cost-effective, suitable for lower-power applications while still achieving excellent heat dissipation.
The heat sink skiving process ensures:
Uniform fin thickness and spacing
Maximum surface area for heat transfer
Strong mechanical integrity without fin detachment
The design of a skived fin heat sink relies on several key principles:
Maximized Surface Area: Skived fins are thin and densely packed, allowing more surface area for convective heat transfer.
Direct Thermal Path: A solid base ensures minimal thermal resistance between the heat source and the fins.
Optimized Airflow: The fins can be aligned to work with natural convection or forced airflow using a heatsink fan.
Customizable Geometry: Custom heatsink options allow fin height, spacing, and orientation to be adjusted for specific thermal requirements.
The combination of skived fin technology and high-quality materials ensures optimal performance even in high-density electronic environments.
| Parameter | Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Copper or Aluminum | High thermal conductivity metals |
| Base Thickness | 3–10 mm | Depends on application power |
| Fin Thickness | 0.1–0.5 mm | Copper skiving for high density |
| Fin Height | 10–50 mm | Adjustable based on airflow and space |
| Fin Spacing | 0.2–1 mm | Optimized for convection or fan cooling |
| Thermal Conductivity | 200–400 W/m·K | Depends on material |
| Cooling Method | Passive or active (heatsink fan) | Optional fan for forced convection |
| Surface Finish | Nickel plating, anodizing, or bare | Enhances corrosion resistance |
Choosing a skived heatsink offers several advantages:
High-efficiency heat dissipation due to skived fin design
Compact design suitable for modern electronics
Enhanced mechanical durability
Ability to integrate with heatsink fan for active cooling
Supports custom heatsink designs for unique thermal challenges
Professional heat sink manufacturers often provide design and engineering support to optimize skiving heat sink performance for specific applications, ensuring both cost-effectiveness and thermal reliability.
Thermal resistance (Rth) is critical for designing skived heatsink solutions. It can be calculated as:
Rhs=PTj−TAMB−Rth−jc−Rinterface
Where:
Tj = Junction temperature
TAMB = Ambient temperature
P = Power dissipation (W)
Rth−jc = Junction-to-case thermal resistance
Rinterface = Thermal interface material resistance
Example: A CPU generating 100 W with Tj=85∘C and TAMB=25∘C, Rth−jc=0.2∘C/W, and thermal interface Rinterface=0.1∘C/W:
Rhs=10085−25−0.2−0.1=0.4∘C/W
This value informs the skived heat sink design to ensure safe operating temperatures.
Skiving heat sinks are ideal for:
CPU and GPU cooling in high-performance computing
Power electronics like inverters, amplifiers, and motor drivers
LED modules and high-power lighting systems
Industrial electronics and telecom equipment
Custom electronics where layout requires custom heatsink solutions
A heat sink is a device designed to dissipate heat from electronic components, maintaining safe operating temperatures and improving reliability.
It uses heat sink skiving to create skived fin heat sink structures. Heat from the component is conducted to the fins, which dissipate it via convection or forced airflow.
Skived heatsinks have thin, densely packed fins for superior thermal performance, while extruded heat sinks typically have thicker, less dense fins.
Copper and aluminum. Skived copper heatsink offers high thermal conductivity, while aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective.
Yes, custom heatsink designs can adjust fin height, spacing, base thickness, and material to meet specific thermal requirements.
High-performance CPUs, GPUs, LED modules, power electronics, industrial and telecom equipment.
Yes, combining with a heatsink fan enhances active cooling and reduces thermal resistance.
Copper skiving allows thinner fins and denser arrays, increasing surface area for better heat dissipation.
It is the process of slicing thin fins from a solid metal block to create skived fin heat sink designs with high thermal efficiency.
Thermal resistance Rhs = (Junction temp – Ambient temp)/Power – Junction-to-case resistance – Interface resistance. See example in the thermal resistance section.
Kingka Tech Industrial Limited
We specialize in precision CNC machining and our products are widely used in telecommunication industry, aerospace, automotive, industrial control, power electronics, medical instruments, security electronics, LED lighting and multimedia consumption.
Address:
Da Long New Village, Xie Gang Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China 523598
Email:
Tel:
+86 137 1244 4018