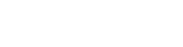In today’s high-performance electronics and computing environments, thermal management is critical. liquid cold plates provide an efficient solution for dissipating heat from CPUs, GPUs, power electronics, and other high-heat components. At KINGKA, we specialize in Custom Cold Plates, offering tailored solutions for a wide range of applications. This article reviews four primary types of liquid cold plates—FSW Liquid Cold Plate, Tube Liquid Cold Plate, Brazed Liquid Cold Plate, and CPU Water Block—covering their working principles, manufacturing processes, materials, costs, advantages, and ideal applications.
1. FSW Liquid Cold Plate

Working Principle
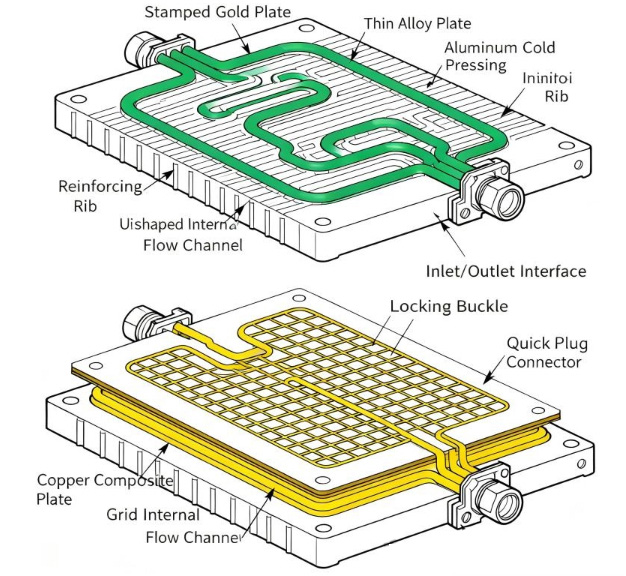
FSW Liquid Cold Plate Parts employ solid-state welding, specifically Friction Stir Welding (FSW), to create integrated cooling channels within the metal block. Heat generated by electronics is transferred directly into the cold plate base, then conducted to the coolant flowing through internal channels. This structure ensures high thermal efficiency and mechanical integrity.
Manufacturing Process
Typical steps in Custom FSW Liquid Cold Plate production:
Design and CNC Machining of internal channel geometry in aluminum or copper blocks (CNC Machined Liquid Cold Plate).
Surface preparation for welding, ensuring flatness and clean interfaces.
Friction Stir Welding of cover plates to form sealed channels.
Leak testing, pressure validation, and flow verification.
Optional post-processing: surface finishing, port threading, and coating.
Materials
Aluminum alloys (e.g., 6061, 7075) for lightweight, high-conductivity plates.
Copper for maximum thermal performance in high-heat-density applications.
Delivery Time and Cost
FSW cold plates require specialized equipment and precision CNC machining. Lead time ranges from 4–8 weeks for prototypes and small batches, with unit cost higher than standard brazed plates but offering superior performance and structural integrity.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
High thermal conductivity and uniform cooling
Strong mechanical integrity due to solid-state welding
Suitable for complex geometries
Disadvantages:
2. Tube Liquid Cold Plate
Working Principle
Tube Liquid Cold Plate Parts use embedded tubes—often copper or aluminum—to circulate coolant. Heat transfers from the base plate into the tube walls, then into the liquid. Some designs use epoxy or other fillers (Epoxy Resin Filling Liquid Cold Plate Manufacturing) to improve thermal contact and structural support.
Manufacturing Process
Bend copper or aluminum tubes to desired serpentine or straight patterns.
Prepare the base plate with grooves or slots for tube placement.
Embed tubes into the base using epoxy or mechanical fixation (Epoxy Resin Filling Liquid Cold Plate).
Seal ports and conduct leak testing.
Materials
Copper tubes for superior conductivity (Copper Tube Liquid Cold Plate Parts)
Aluminum tubes for lightweight, cost-sensitive applications
Delivery Time and Cost
Tube cold plates are simple to produce and cost-effective for small- to medium-volume orders. Lead time typically 2–6 weeks, depending on customization and epoxy curing.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
Low cost and rapid production
Flexible tube arrangements for varied geometries
Suitable for low to moderate heat flux applications
Disadvantages:
Lower thermal efficiency compared to CNC-machined or FSW plates
Thermal uniformity may be less ideal
Epoxy may degrade over long-term high-temperature exposure
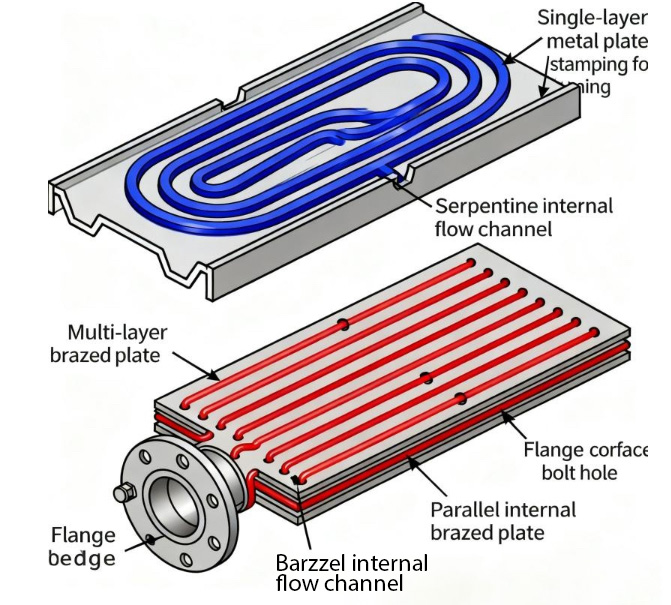
3. Brazed Liquid Cold Plate
Working Principle
Brazed Liquid Cold Plate systems rely on vacuum brazing to join the base plate and cover with internal cooling channels. Heat is conducted directly into the channels, and the brazed joints ensure leak-tight, high-pressure capabilities.
Manufacturing Process
Stamp or machine base and cover components.
Apply brazing foil or paste at contact interfaces (Vacuum Brazing Liquid Cold Plate, Vacuum Brazed Cold Plate).
Stack and align the assembly.
Perform vacuum brazing in a controlled furnace.
Conduct pressure tests, flow testing, and surface finishing.
Materials
Aluminum alloys for lightweight, high-volume applications
Copper for applications requiring maximum thermal performance (Copper Tube Liquid Cold Plate Parts)
Delivery Time and Cost
Brazed cold plates are cost-effective for medium to high-volume production. Lead times range from 3–8 weeks, depending on batch size and complexity. Unit cost is moderate, with excellent scalability.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
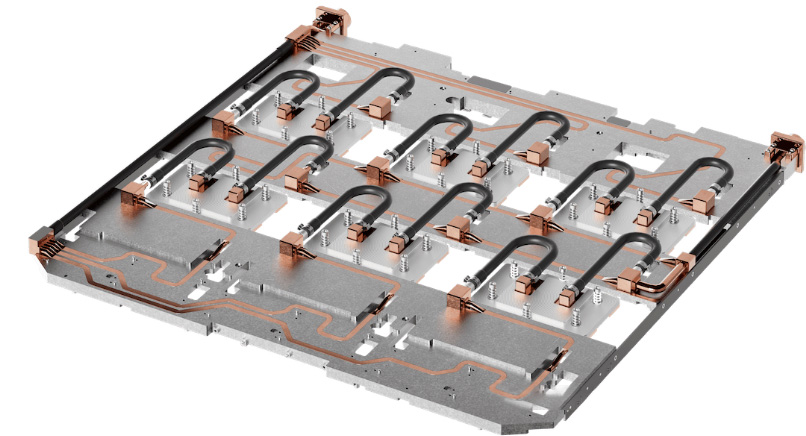
4. CPU Water Block
Working Principle
CPU Water Blocks directly contact the CPU die or GPU die, transferring heat into microchannels or fin arrays. Coolant flows through these channels to dissipate heat efficiently. Popular designs include GPU Cold Plate, Birch Stream Cold Plate, and Eagle Stream Cold Plate, each optimized for specific heat flux patterns.
Manufacturing Process
CNC machine microchannels or fin arrays in copper or aluminum.
Attach cover plate via soldering, brazing, or mechanical compression.
Perform pressure testing and flow verification.
Optional plating (nickel or other coatings) for corrosion resistance.
Materials
Delivery Time and Cost
Highly customized CPU water blocks typically require 2–6 weeks for prototypes and small batches. Costs are higher per unit due to precision CNC machining and microchannel complexity.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
Excellent localized heat removal
Can be tailored for CPUs, GPUs, or custom electronics
High performance for high-density computing
Disadvantages:
Comparative Summary
| Cold Plate Type | Thermal Performance | Cost | Customizability | Typical Application |
|---|
| FSW Liquid Cold Plate | High | High | Medium | High-end GPUs, AI accelerators |
| Tube Liquid Cold Plate | Medium | Low | High | Industrial systems, low-heat applications |
| Brazed Liquid Cold Plate | Medium-High | Medium | Low-Medium | Data center servers, mass production electronics |
| CPU Water Block | Very High | High | High | CPUs, GPUs, AI accelerators |
Application Mapping
FSW Liquid Cold Plate: High-power AI/GPU accelerators, compact form factor devices
Tube Liquid Cold Plate: Industrial cooling, low-cost liquid cooling systems, small embedded devices
Brazed Liquid Cold Plate: Server racks, telecom equipment, moderate heat density applications
CPU Water Block: Desktop CPUs, high-end GPUs, custom electronics, gaming or workstation applications
Trends and Future Directions
Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining FSW, CNC machining, and brazing for optimal thermal and mechanical performance.
High-Density Microchannel Plates: Increasing thermal efficiency in compact AI/GPU applications.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: Customized internal geometries for prototypes and low-volume production.
Advanced Sealing Technologies: Vacuum brazing, FSW, and epoxy resin filling for reliable, leak-proof operation.
Material Innovation: Integration of copper-aluminum hybrid structures for cost-effective high thermal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Which cold plate offers the best thermal performance?
A1: CPU Water Blocks and FSW Liquid Cold Plates offer the highest thermal efficiency due to optimized microchannels and solid-state welded structures.
Q2: Which cold plate type is fastest for prototyping?
A2: Tube Liquid Cold Plate and CNC FSW Liquid Cold Plate designs can be rapidly produced without expensive molds.
Q3: Can brazed cold plates handle high-pressure coolants?
A3: Yes. Vacuum Brazed Cold Plates are leak-proof and can withstand high-pressure applications commonly found in data centers.
Q4: Should I choose copper or aluminum?
A4: Copper provides superior thermal conductivity for high heat flux applications. Aluminum offers lower weight and cost, suitable for low to medium heat flux requirements.