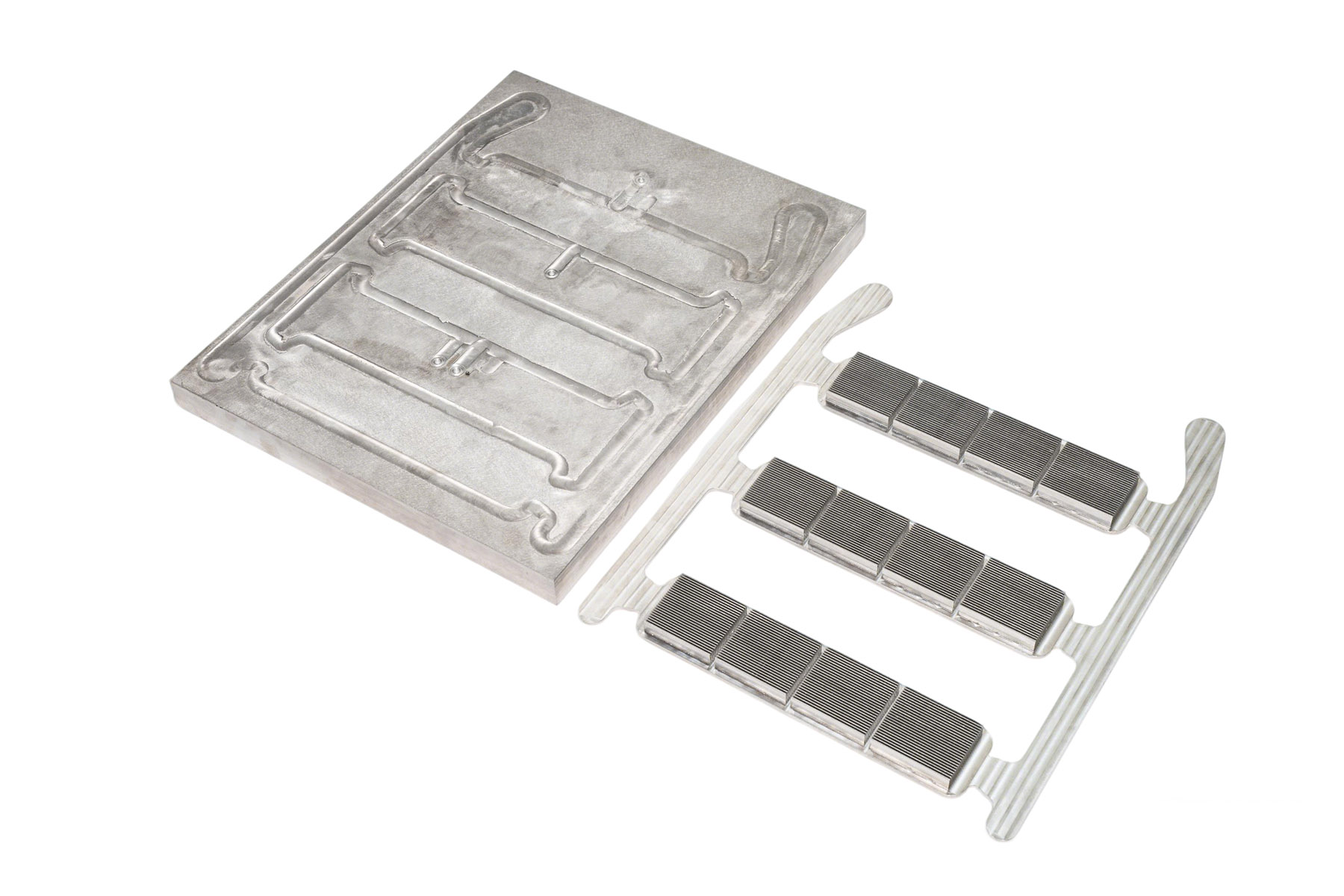
Vacuum-brazed aluminum cold plates are widely used in battery thermal management, power electronics cooling, new-energy vehicles, and high-density servers. As a professional Vacuum Brazing Liquid Cold Plate manufacturer and Vacuum Brazing liquid cold plate supplier, we provide an in-depth overview of how material selection and brazing process control determine the quality and performance of liquid cold plates.

1. Why Vacuum Brazing Is Critical for Liquid Cold Plates
Vacuum brazing is performed under a high vacuum environment (≤10⁻³ Pa), without using flux. This prevents oxidation and ensures a clean, high-strength, leak-free internal channel—critical for any liquid cooling plate or Brazed Liquid Cold Plate. The process offers several advantages:
Production of extremely clean joints
Excellent capillary flow of filler metal
High reliability for complex internal channels
Suitable for thin-walled and multi-layer structures
Ideal for thermal management cold plate applications requiring long-term stability
Compared with mechanical joining or TIG welding, vacuum brazing is currently the most reliable technology for manufacturing liquid cooled cold plates used in EV battery packs, telecom modules, and industrial inverters.
2. Characteristics of 3003 Aluminum Alloy in Vacuum Brazing
Material Overview
3003 is an Al-Mn alloy with:
Vacuum Brazing Behavior of 3003
3003 performs excellently in Vacuum brazing cold plate manufacturing due to its stable structure and lack of volatile elements.
Key characteristics:
Mn refines grains and improves brazing stability
Fewer defects and less erosion when temperature is controlled at 580–590°C
Suitable for thin-walled designs such as honeycomb cores and high-flow cooling channels
This makes 3003 ideal for brazed cold plate designs that prioritize manufacturability and corrosion resistance.
3. Characteristics of 6061 Aluminum Alloy in Vacuum Brazing
Material Overview
6061 is an Al-Mg-Si alloy that:
Vacuum Brazing Behavior of 6061
The main challenge is Mg volatilization at brazing temperature (≈588°C).
Mg evaporation can:
Contaminate the vacuum chamber
Influence filler metal wetting behavior
Narrow the allowable temperature window
Therefore, when designing custom liquid cold plate or high-load high-performance cold plate using 6061, strict control of the following is essential:
Although the process is more demanding, 6061 offers superior mechanical strength—ideal for liquid cold plates used in aerospace, EV battery structural cooling panels, and high-power semiconductor modules.
4. Key Vacuum Brazing Process Parameters for Liquid Cooling Plates
(1) Filler Metal Selection
Common filler metal: 4004 (Al–Si–Mg)
For 6061 structures requiring lower temperatures, advanced low-melting Al-Si-Cu-Mg fillers (514–538°C) can effectively reduce overheating and grain growth.
(2) Temperature and Holding Time
Temperature is the most critical parameter:
Too low → Poor melting, weak bonding
Too high → Base metal erosion, honeycomb dissolution, Mg volatilization (6061)
Holding time must complement temperature and filler metal diffusion behavior.
(3) Degree of Vacuum (≤10⁻³ Pa)
High vacuum eliminates oxide film and ensures clean seam formation.
(4) Surface Cleanliness and Fit-Up Gap
(5) Tooling and Fixturing
Good fixture design helps:
These factors are critical because a single tiny leak inside a brazed liquid cold plate can cause catastrophic failure in EV or industrial cooling systems.
5. Common Defects and Solutions in Brazed Cold Plates
1. Excess Filler Flow (Solder Overflow)
Reasons: Excessive temperature, long holding time, small grain size
Solutions:
2. Base Metal Erosion
Reasons: Over-temperature, long soak time, filler melting point too close to base metal
Solutions:
3. Poor Weld Formation / Porosity
Reasons: Insufficient vacuum, contamination, improper clearance
Solutions:
Improve surface cleaning
Optimize vacuum system
Adjust joint design
6. Material Selection Guide for Liquid Cold Plates
When to choose 3003 cold plates
High corrosion resistance required
Complex internal channels
Cost-effective thermal management
EV battery cooling, heat exchangers, telecom modules
When to choose 6061 cold plates
High strength or structural load needed
Aerospace and defense electronics
High-pressure coolant systems
High-power IGBT or inverter modules
3003 provides a wider process window, while 6061 provides higher joint strength—both suitable for brazed liquid cold plate solutions, depending on your application.
7. How Liquid Cold Plates Work (Overview)
A liquid cold plate uses circulating coolant inside precision-engineered internal channels or micro-channels to absorb and transfer heat away from electronic components.
Working principle:
Heat enters the cold plate base (usually 3003 or 6061 aluminum).
Coolant flows through internal channels formed by vacuum brazing.
Heat is transferred to the coolant by conduction and convection.
The heated coolant exits and is cooled by a radiator or chiller.
This mechanism provides significantly better heat dissipation than natural convection or heatsinks alone, making cold plate liquid cooling the preferred choice for high-power electronics.
Vacuum brazing is essential for manufacturing high-performance cold plates with reliable, leak-free channels.
With optimized filler metals, strict temperature control, and precision fixtures, both materials can deliver excellent results in brazed cold plates, liquid cooling plates, and custom liquid cold plates.
As an experienced Vacuum Brazing Liquid Cold Plate manufacturer and supplier, we offer comprehensive design, machining, and brazing solutions tailored for EV, telecom, aerospace, industrial automation, and high-power electronics cooling.