In the world of electronics, managing heat is critical. Excessive heat can reduce performance, shorten component lifespan, or even lead to permanent damage. That’s where the heat sink comes in—a seemingly simple device that plays a vital role in thermal management across a wide range of industries, from consumer electronics to aerospace.

What Is a Heat Sink?
A heat sink is a passive cooling device designed to absorb heat from an electronic component and dissipate it into the surrounding environment, usually air or liquid. By conducting heat away from critical components like CPUs, power transistors, or LED modules, heat sinks maintain optimal operating temperatures, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
Heat sinks can vary widely in material, design, and size. Aluminum heat sinks are popular for their lightweight structure, good thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness. Copper heat sinks, including skived copper heatsinks, offer higher thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-performance or compact electronics where heat density is high.
How Does a Heat Sink Work?
The operation of a heat sink relies on three primary heat transfer mechanisms:
Conduction – Heat is transferred from the hot electronic component to the heat sink material. High-conductivity metals like aluminum or copper ensure rapid and efficient heat flow.
Convection – Heat is then transferred from the heat sink surface to the surrounding air or liquid. The presence of heat sink fins greatly increases surface area, enhancing airflow and cooling efficiency.
Radiation – A small amount of heat is emitted as infrared radiation. Surface treatments, such as anodizing, nickel plating, or powder coating, can improve heat radiation and protect the heat sink from corrosion.
By maximizing these mechanisms, heat sinks ensure that electronic components remain within safe temperature ranges, even under heavy loads.
Types of Heat Sinks
Aluminum and Copper Heat Sinks
Aluminum heatsinks are widely used due to their lightweight nature, ease of manufacturing, and effective heat conduction. They are ideal for applications ranging from CPU heat sinks in computers to LED lighting and consumer electronics.
Copper heat sinks provide superior thermal conductivity, up to nearly twice that of aluminum. Skived copper heatsinks are often used in high-performance applications, such as industrial power electronics, automotive electronics, and aerospace systems, where rapid heat dissipation is critical.
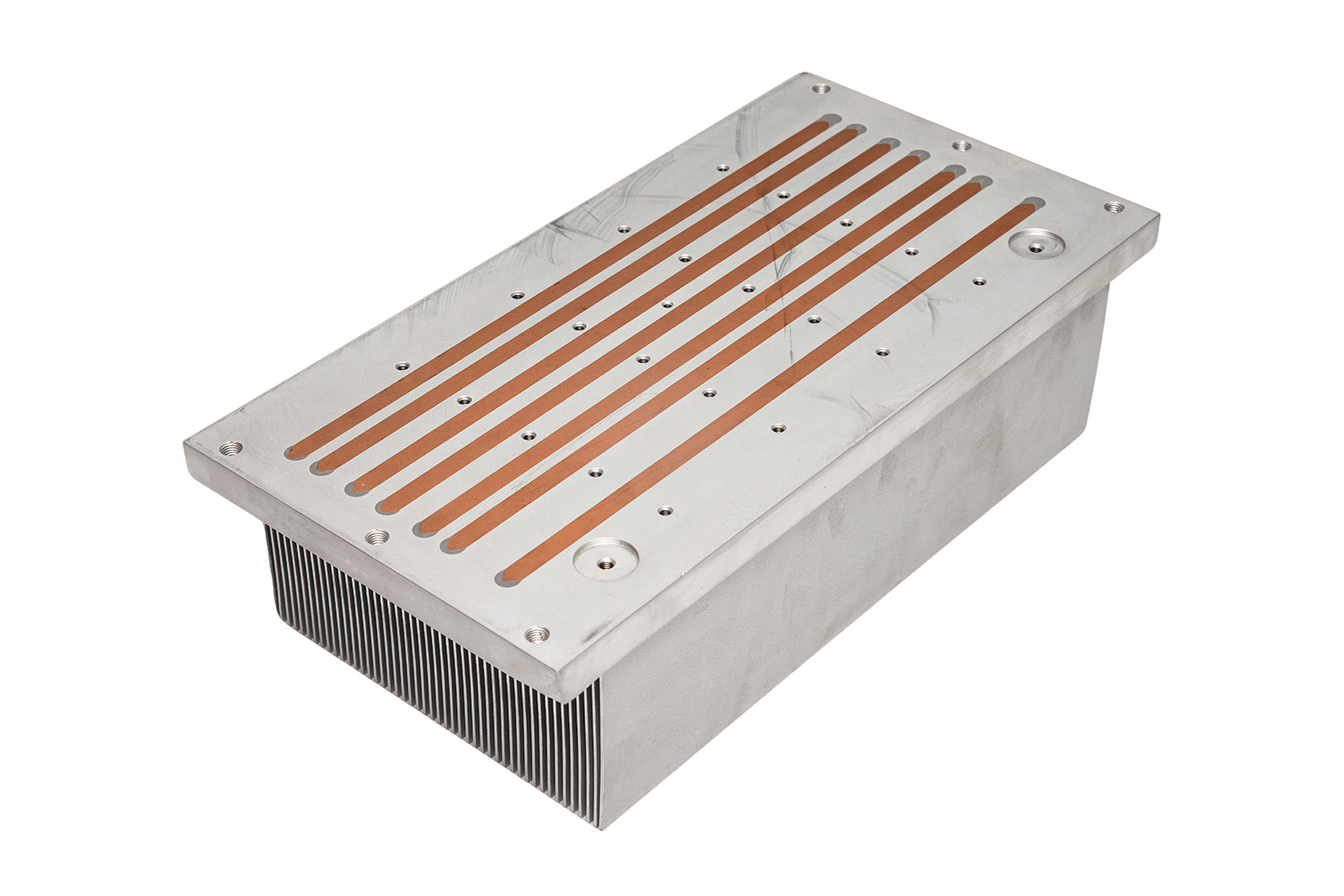
An extruded heat sink is produced by forcing aluminum through a die, creating a profile with integrated fins. These fins increase the surface area, improving cooling efficiency. Extrusion is cost-effective for standard designs but may have limitations in fin density and customization compared to advanced techniques.
Skived fin heat sinks are made by slicing ultra-thin fins directly from a solid block of aluminum or copper. This allows extremely high fin density and excellent thermal performance. The continuous base-to-fin structure ensures robust mechanical integrity and uniform heat transfer. Skived fin heat sinks are ideal for custom heatsink designs in compact electronics or high-power applications.
Flexible Heat Sinks and Heat Spreaders
Modern applications sometimes require flexible heat sinks or aluminium heat spreaders. Flexible heat sinks conform to irregular surfaces, making them suitable for devices with spatial constraints. Heat spreaders distribute heat evenly across a larger area, preventing hotspots and improving overall thermal performance.
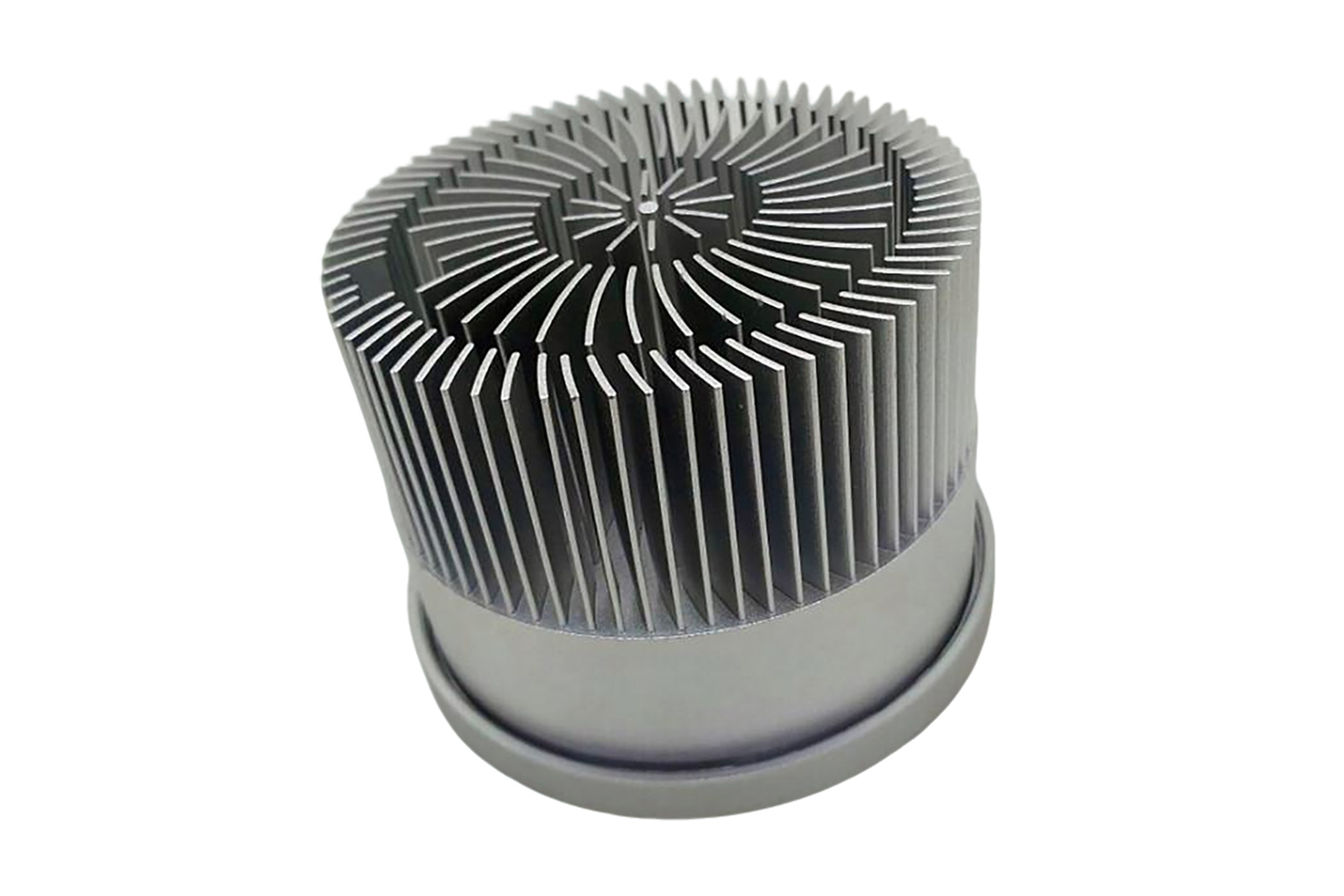

Heat Sink Design Considerations
When selecting a heat sink, several factors must be considered:
Material: Aluminum for lightweight and general applications, copper for high-performance or high-density devices.
Fin Design: Higher fin density increases surface area and improves heat transfer.
Size and Shape: Must fit within the device’s enclosure while maintaining airflow.
Surface Treatment: Anodizing, nickel plating, or powder coating enhances corrosion resistance and heat radiation.
Mounting Method: Thermal pads, screws, clips, or adhesives ensure proper contact with the heat source.
Companies specializing in thermal management, including heat sink suppliers and aluminium heat sink manufacturers, often provide custom heatsink manufacturing services to optimize performance for specific applications.
Applications of Heat Sinks
Heat sinks are essential in a wide range of industries:
Computing: CPU heat sinks in desktops, laptops, and servers prevent overheating of processors.
Telecommunications: Cooling equipment such as base stations, routers, and networking servers.
Automotive Electronics: Managing heat in EV controllers, inverters, and LED headlights.
Industrial Control: Power modules in PLCs, variable frequency drives, and industrial machinery.
LED Lighting: High-power LED modules require efficient aluminum heatsinks to maintain brightness and longevity.
Medical Devices: Diagnostic and imaging equipment rely on stable temperatures for accuracy.
Consumer Electronics: Gaming consoles, amplifiers, and projectors benefit from effective heat dissipation.
Heat Sink Manufacturing Process
The heat sink manufacturing process typically involves:
Material Selection: Choosing high-purity aluminum or copper based on thermal requirements.
Shaping: Using extrusion, skiving, or CNC Machining to form fins and the base.
Surface Treatment: Anodizing, nickel plating, or powder coating improves durability and thermal radiation.
Inspection & Testing: Thermal resistance and mechanical stability tests ensure reliability.
Companies such as custom heatsink manufacturers and aluminum heat sink suppliers offer tailored solutions, including custom heatsink design, OEM/ODM services, and thermal simulation to meet specific project requirements.
A heat sink may seem like a simple component, but it plays a critical role in modern electronics. From CPU heat sinks to skived fin heat sinks and aluminium heat spreaders, effective thermal management ensures device performance, reliability, and longevity. By choosing the right material, design, and manufacturer, engineers can optimize cooling for a wide range of applications—from consumer electronics to industrial power modules and automotive systems.
With advancements in heat sink manufacturing processes, companies like professional heat sink suppliers and custom heatsink manufacturers continue to provide innovative, high-performance thermal solutions for global industries.