If you have ever stood near a large solar inverter or an EV fast-charging station and felt the stream of hot air being pushed out, you have experienced first-hand the byproduct of high-power electronics—waste heat. In our rapidly electrifying world, power levels are increasing, and so is the thermal challenge. A smartphone processor may only need a small heat spreader, but when a system is managing power equivalent to what could run a neighborhood, thermal management becomes a mission-critical engineering problem.
This is where big heat sinks enter the picture. These are not ordinary aluminum blocks; they are precision-engineered thermal management systems that quietly ensure the reliability of renewable energy infrastructure, high-density data centers, and electric vehicle fast-charging networks.
Understanding these large-scale thermal solutions is crucial for engineers and product designers developing the next generation of power electronics.
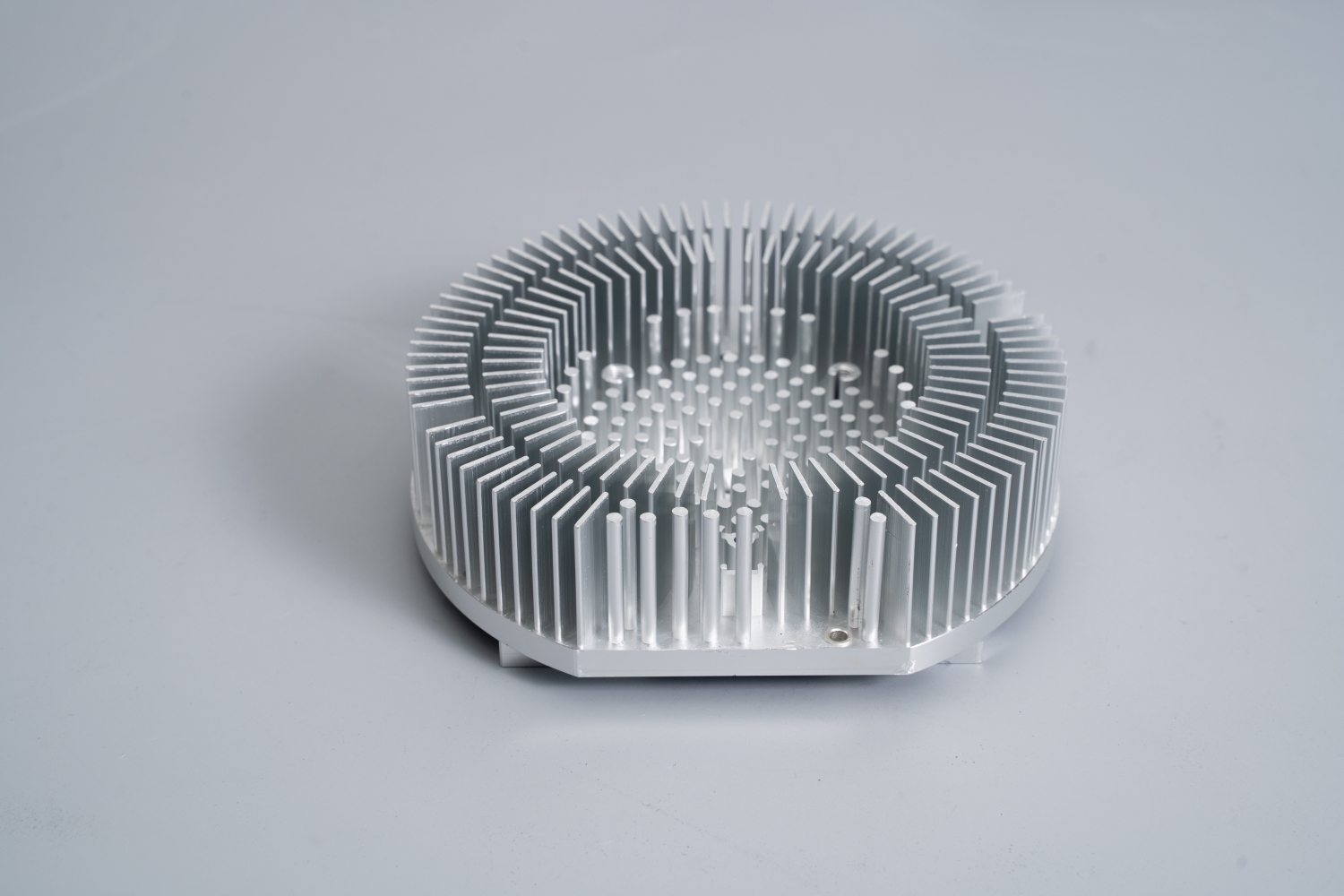

What Defines a “Big Heat Sink” in Modern Thermal Management?
A “big heat sink” is defined by function and performance, not just physical size. These are thermal solutions designed for systems that dissipate hundreds or even thousands of watts of heat. Key defining features include:
Massive Surface Area – Maximizing heat transfer area through tightly packed fins, complex geometries, or hybrid materials.
High Thermal Mass – Using large aluminum or copper structures to absorb transient thermal spikes and stabilize temperature profiles.
Advanced Manufacturing – skived fin, bonded fin, brazed assemblies, or friction stir welded cold plates ensure maximum efficiency and structural integrity.
Forced Convection or Liquid Cooling – Integration with high-static-pressure fans or coolant loops to enable high-density heat removal.
This engineering approach enables thermal resistances that standard extruded profiles simply cannot achieve.
When Standard Cooling Isn’t Enough
Extruded aluminum heat sinks are perfect for low-to-moderate power applications (typically<100w). but="" extrusion="" has="" geometric="" limitations="">
When dealing with IGBT modules in solar inverters, high-wattage RF amplifiers, or power supplies in 5G base stations, you quickly exceed the safe limits of conventional solutions. Heat density rises, and thermal margin disappears. At this stage, you must transition to large-scale custom thermal designs—what we call “big heat sinks.”
Key Engineering Characteristics
To handle multi-kilowatt thermal loads, large heat sinks integrate several engineering principles:
Dense Fin Arrays for Maximum Surface Area
Skived or bonded fin technologies create high aspect-ratio fins that maximize convection efficiency per unit volume.
Thermal Mass & Stability
The baseplate acts as a heat spreader, smoothing out temperature fluctuations and protecting sensitive components.
Optimized for Forced Convection
Fin geometry is tuned for pressure drop vs. airflow, and paired with high-performance fans or blowers for predictable performance.
Beyond Air Cooling: Liquid Cold Plates
When power levels exceed what air can dissipate, thermal engineers turn to liquid cooling solutions. Liquid cold plates provide:
10x the Heat Transfer Efficiency of Air
Compact Footprint for high-density electronics
Scalable Design for applications like EV battery packs, BESS modules, and HPC server racks
Manufacturing methods such as vacuum brazing and Friction Stir Welding (FSW) ensure leak-proof, high-reliability solutions suitable for automotive, aerospace, and telecom-grade applications.
Industries That Depend on Big Heat Sinks
Big heat sinks are an enabling technology for some of the world’s most demanding industries:
Renewable Energy – Central PV inverters and wind turbine converters dissipate tens of kilowatts of heat.
Data Centers & Cloud Computing – Modern racks exceed 50kW, requiring cold plates for CPUs, GPUs, and ASICs.
EV & Energy Storage – DC fast chargers (up to 350kW) and grid-scale battery systems require robust thermal protection.
Telecom & Power Electronics – 5G base stations and industrial drives demand reliable, outdoor-rated cooling hardware.
Advanced Manufacturing for Maximum Performance
Big heat sinks are built using techniques that push past the limits of extrusion:
Bonded Fin Heat Sinks – Aluminum or copper fins epoxied or soldered into a machined base, achieving high fin density and mixed-metal designs.
Skived Fin Heat Sinks – Fins cut directly from a solid block, resulting in seamless thermal conductivity and minimal thermal resistance.
Vacuum Brazed Liquid Cold Plates – Multi-layer assemblies joined in a furnace for a lightweight, leak-proof solution.
FSW Cold Plates – Ideal for automotive-grade reliability where vibration and pressure cycling are concerns.
Each method is selected based on performance requirements, cost targets, and production volume.
Key Design Considerations
When specifying a big heat sink, engineers must balance:
Thermal Resistance vs. Airflow Pressure Drop – Matching fin density to fan capability for optimal system-level performance.
Material Choice – Copper for heat spreading, aluminum for weight savings and cost efficiency, or hybrid designs for both.
Mechanical Strength – Ensuring the assembly can withstand vibration, shock, and mounting stress.
Total Cost of Ownership – Weighing up-front cost against long-term reliability, maintenance, and potential downtime.
Why Custom Solutions Win Over Off-the-Shelf Designs
For high-power projects, custom thermal solutions deliver:
Up to 30% better thermal performance through simulation-driven optimization.
Reduced footprint and weight via geometry tailoring.
Lower total system cost by preventing thermal-related failures and improving efficiency.
Tools like Ansys Icepak and Flotherm enable full-system CFD analysis, hotspot detection, and parametric optimization before any tooling is cut.
Choosing the Right Thermal Partner
A successful project requires a true engineering partner, not just a vendor. Look for:
Full In-House Capabilities – CNC Machining, fin manufacturing, brazing, FSW, and surface finishing under one roof.
Experienced Engineering Team – Veterans who understand thermal simulation, DFM, and complex mechanical integration.
Rapid Prototyping & Testing – Ability to deliver samples in 3–4 weeks for early validation.
Global-Grade Quality Certifications – ISO9001, ISO14001, and IATF16949 compliance for automotive and mission-critical applications.
Partner with Kingka Tech
At Kingka Tech, we combine cutting-edge simulation, precision manufacturing, and industry expertise to deliver thermal solutions for the most demanding applications. From high-density skived fin heat sinks to brazed liquid cold plates, we provide end-to-end solutions that unlock performance, improve reliability, and reduce risk.
If you are developing the next generation of high-power electronics, don’t settle for an off-the-shelf cooler. Partner with us to design a custom-engineered solution that keeps your system running cool, efficient, and reliable.