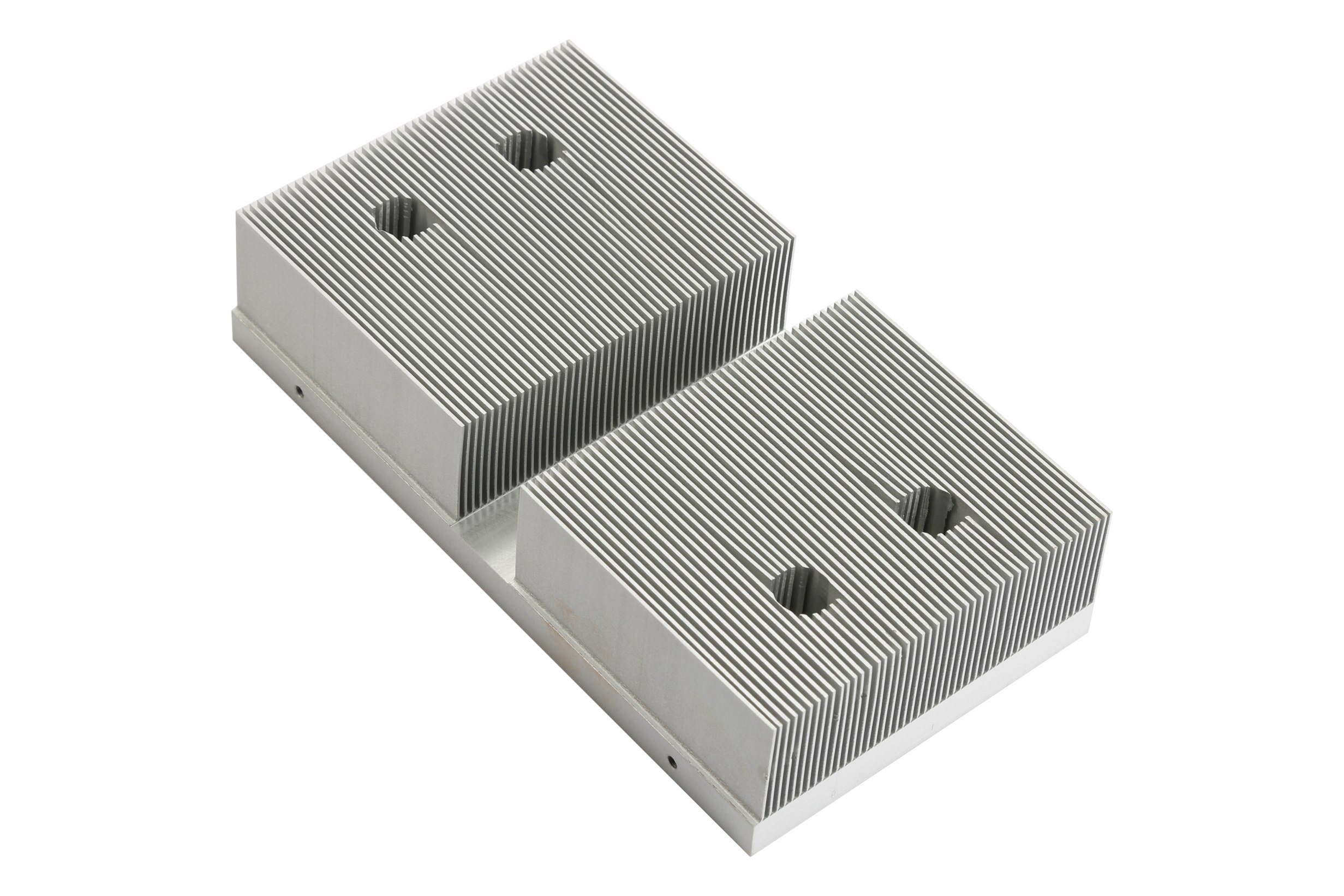



heat sinks are Heat sink components used to transfer heat generated by electronic components to the air. They are widely used in electronics, automobiles, communications, energy and other fields. The manufacture of heat sinks involves multiple links such as design, material selection, processing technology and surface treatment. As a professional custom heat sink manufacturer, KingKa provides high-precision heat sink solutions to meet customers' heat dissipation needs in different application scenarios.
Manufacturing machines and equipment
The manufacture of heat sinks uses a variety of precision equipment, mainly including:
CNC processing equipment: Computer numerical control (CNC) equipment is used to accurately cut and process various shapes and sizes of heat sinks to ensure the accuracy and complex design of heat sinks.
Die casting equipment: Die casting is a common method for producing heat sinks with complex geometric shapes. It is mainly used for aluminum alloy heat sinks. The molten metal is injected into the mold under high pressure, with high precision and high consistency.
Extrusion equipment: Aluminum extrusion is a method commonly used in heat sink production. By heating the aluminum ingot and pushing it through the mold, a long strip of heat sink profile is formed, which has a good surface area and helps to dissipate heat.
Welding and assembly equipment: For heat sinks that require multi-component assembly, such as the connection of heat pipes and base plates, welding equipment is used for high-precision assembly to ensure the stability and heat dissipation efficiency of the heat sink.
Manufacturing process
Design and prototyping: The design of the heat sink is application-oriented, and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is usually used for thermal analysis and optimization. Depending on the specific application, the shape, size and heat dissipation performance can be customized.
Material selection: The material of the heat sink directly affects its heat dissipation performance. Common materials include:
Aluminum alloy: Aluminum has good thermal conductivity, light weight and cost-effectiveness, and is the most commonly used heat sink material. Aluminum alloys such as 6061 and 6063 are often used for extrusion and die casting.
Copper: Copper has better thermal conductivity than aluminum, but the price is higher, which is suitable for high-performance heat dissipation needs.
Copper-aluminum composite: The design of copper base with aluminum fins takes into account both heat dissipation performance and cost.
Precision machining: After selecting the right material, the heat sink will be precision machined by CNC machining, extrusion or die casting to ensure accurate size and surface quality.
Surface treatment: In order to improve the corrosion resistance and heat dissipation performance of the radiator, surface treatment is usually performed. Common treatment methods include:
Anodizing: An oxide film is formed on the aluminum surface by electrochemical methods to enhance corrosion resistance and increase surface area, thereby improving heat dissipation.
Powder coating: Powder coating increases the appearance and protection of the radiator. Although it does not directly affect the heat dissipation effect, it can prevent oxidation corrosion.
Nickel plating: Copper radiators are often treated with nickel plating to prevent oxidation and improve thermal conductivity.
Quality control and testing: After the radiator is processed, it needs to pass strict thermal testing, dimensional testing and material inspection to ensure that its performance meets the design requirements and ensures the stable operation of the product in different environments.
Precision and tolerance
The precision of the radiator is critical, especially in applications that require precise matching with other components. Precision machining and high-precision CNC equipment can ensure that the size and surface quality of the radiator meet strict tolerance requirements, ensure that the components are properly installed and dissipate heat effectively. In some critical applications, such as medical equipment and aerospace, the high precision of the radiator directly affects the reliability and durability of the equipment.
Finished product optimization
The final effect of the heat sink depends not only on its manufacturing process, but also on a series of optimization measures to improve the heat dissipation performance:
Fin design: The shape, density and thickness of the fins directly affect the heat dissipation efficiency. By optimizing the fin design, the surface area of the heat sink can be increased, thereby improving the thermal conductivity.
Thermal interface material (TIM): Thermal paste, thermal pads and other materials can be applied between the heat sink and electronic components to enhance the heat conduction efficiency.
Combined with other cooling systems: Sometimes, the heat sink needs to be used in combination with fans, heat pipes or liquid cooling systems to optimize the entire heat dissipation system to improve thermal management efficiency.
Application scenarios
Heat sinks are widely used in many industries and fields. Here are some typical applications:
Consumer electronics: In devices such as smartphones, laptops, and game consoles, heat sinks are used to cool processors and graphics processing units (GPUs) to prevent overheating and improve the performance and service life of the device.
Automotive industry: Automotive electronic components, such as power control units and LED lighting systems, often rely on heat sinks to keep the system running stably.
Communications Industry: In telecommunications equipment, heat sinks are used to cool power amplifiers and RF components to ensure stable signal transmission.
Industrial and Military: In industrial and military equipment, heat sinks are used to manage the thermal load of power electronics to ensure the reliability of critical equipment.
Renewable Energy: In solar systems and other renewable energy applications, heat sinks are used in components such as power inverters to improve system efficiency and extend equipment life.
Features and Benefits
Efficient heat dissipation: The core function of a heat sink is to effectively transfer heat from electronic components to the environment. By increasing the surface area and optimizing airflow, heat sinks can quickly and effectively dissipate heat.
Cost-effectiveness: Compared with liquid cooling or refrigeration systems, heat sinks are a more cost-effective and easy-to-implement solution for equipment with moderate heat requirements.
Durability: High-quality aluminum or copper heat sinks have good corrosion resistance and durability, and can be used for a long time in a variety of environments with reduced maintenance frequency.
Customization: KingKa's custom heat sinks provide customers with tailor-made solutions, including unique shapes, sizes and heat dissipation properties to suit different application requirements.
Heat sink manufacturing is a complex process that involves design optimization, precision machining, material selection, and surface treatment. By using high-precision equipment such as CNC processing machines, die-casting machines, and extrusion equipment, KingKa is able to produce custom heat sinks that meet customer needs. These heat sinks not only play a vital role in improving device performance, but also ensure the stability and long-term reliability of equipment in a variety of industries. Whether in consumer electronics, automotive, communications, or industrial fields, custom heat sinks are an important part of ensuring the efficient operation of equipment.
Kingka Tech Industrial Limited
We specialize in precision CNC machining and our products are widely used in telecommunication industry, aerospace, automotive, industrial control, power electronics, medical instruments, security electronics, LED lighting and multimedia consumption.
Address:
Da Long New Village, Xie Gang Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China 523598
Email:
Tel:
+86 137 1244 4018