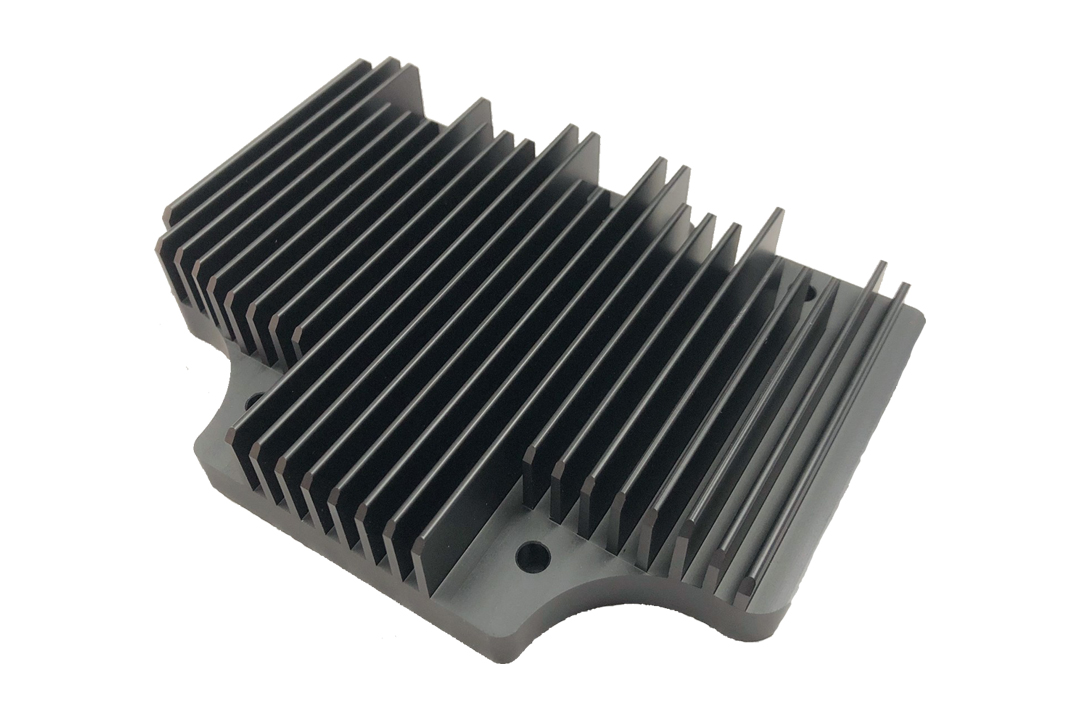



An extruded heat sink is a cooling device that primarily transfers heat away from electronic components, thereby ensuring that these devices do not overheat. The extrusion process is done by increasing the surface area of the heat sink by heating the material (usually aluminum) and squeezing it through a die to form the desired profile. This increase in surface area helps to dissipate heat more efficiently.
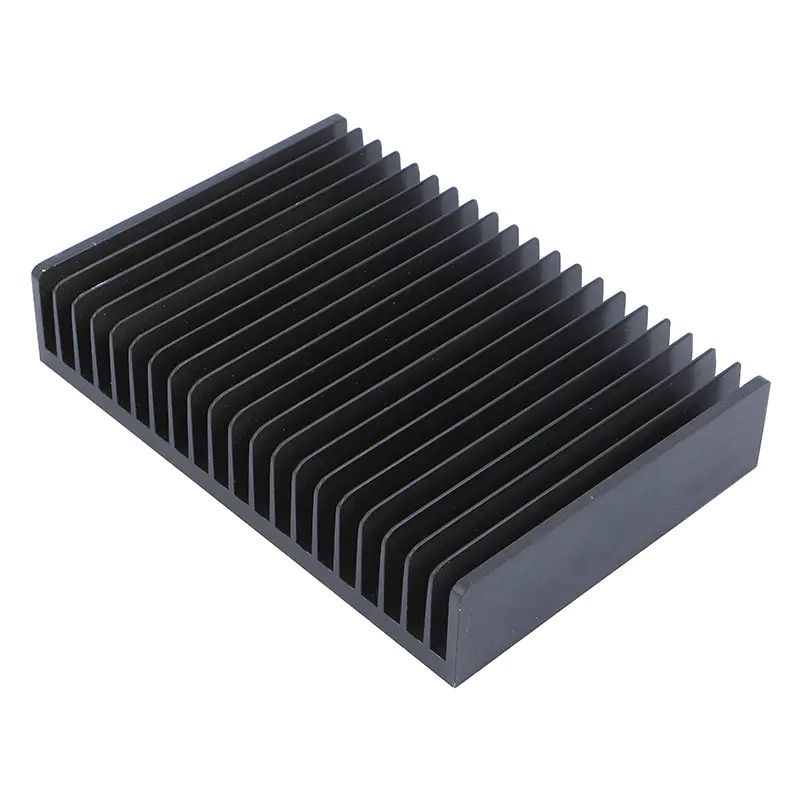

Manufacturing process of an extruded Heat Sink:
Material selection: The most commonly used material is aluminum due to its excellent thermal conductivity, light weight, and ease of processing. However, copper and other alloys can also be used in applications that require higher thermal conductivity.
Extrusion process: In this process, a block of aluminum is heated to a semi-molten state and then extruded through a die into the desired shape. This method allows manufacturers to mass-produce Heat Sinks with consistent shapes and sizes.
Post-Extrusion Operations: After extrusion, the heat sink may undergo secondary operations such as cutting, machining, or punching to achieve the desired size and add features such as mounting holes or fan mounting slots.
Key Features of Extruded Heat Sinks
Thermal Conductivity: The main function of a heat sink is to dissipate heat away from sensitive electronic components. The thermal conductivity of the material used (usually aluminum) is a key factor in the effectiveness of the heat sink. Aluminum alloys generally have a thermal conductivity between 150 and 220 W/m·K, which is sufficient for most electronic applications.
High Surface Area: Extruded heat sinks are designed with many fins or extended surfaces that increase the contact area with the air, thereby enhancing the heat dissipation effect. The size, shape and spacing of these fins can be adjusted according to the requirements of the cooling system.
Lightweight and Durable: The extrusion process can produce lightweight and strong structures. Aluminum has strong corrosion resistance and can maintain structural integrity in harsh environments, which makes extruded heat sinks ideal for long-term use.
Precision and Customization: Extruded heat sinks have a high degree of precision, which ensures the accuracy of dimensions during the manufacturing process. This is essential for the heat sink to fit tightly with the electronic component, thereby maximizing the heat sink's surface area and heat dissipation efficiency. Manufacturers can customize the heat sink profile to meet specific application needs and integrate additional features such as mounting holes or fan slots.
Precision and Surface Treatment
Precision: The extrusion process is known for its high precision, which is essential for manufacturing heat sinks that can precisely fit electronic components. Exact dimensions and tolerances are essential for the effective performance of the heat sink, ensuring that it fits tightly to the component being cooled, thereby maximizing the heat dissipation.
Surface Treatment
Anodizing: Anodizing forms a protective oxide film on the surface of aluminum through an electrochemical reaction. This treatment enhances the corrosion resistance, wear resistance and thermal conductivity of the heat sink.
Painting: Painting provides a durable and aesthetic surface for the heat sink. It also provides additional protection against corrosion, which is essential for heat sinks exposed to environmental factors.
Nickel Plating: For heat sinks made of copper or other metals, nickel plating can increase the surface's corrosion resistance and improve appearance.
Clear Coating: Some heat sinks are coated with a clear coating to preserve the metal's natural appearance and improve its resistance to oxidation.
These surface treatments enhance the performance of the heat sink, extend its life, and improve its appearance.
Applications of Extruded Heat Sinks
Consumer Electronics: Extruded heat sinks are widely used in consumer electronics products such as computers, smartphones and TVs. They are used to cool processors, graphics cards and power supplies, helping to keep the device running smoothly and prevent overheating.
LED Lighting: LED lamps generate a lot of heat when working, and extruded heat sinks are often used in LED lamps to maintain the optimal operating temperature of LED drivers and chips.
Automotive Industry: In the automotive field, extruded heat sinks are used in various applications such as power control units (PCUs), electric vehicle (EV) battery management systems, and electronic control units (ECUs). These components require effective heat dissipation to prevent failures due to overheating.
Communication Industry: In the communications field, heat sinks are used to cool power amplifiers, routers and other high-performance communication equipment. The cooling effect provided by heat sinks is crucial to ensure the reliable performance of network equipment.
Medical Equipment: Medical equipment such as MRI machines, X-ray equipment and diagnostic systems often use extruded heat sinks to maintain their normal operation and prevent overheating during long-term use.
Industrial Applications: Extruded heat sinks are used in various industrial equipment such as power supplies, motor drives and control panels, where thermal management is crucial for the long-term and efficient operation of the equipment.
Common Problems with Extruded Heat Sinks
Thermal Resistance: In some cases, heat sinks may not dissipate heat efficiently due to improper design or high thermal resistance of the material. This requires selecting the right material to ensure that its thermal conductivity is optimized.
Size and Fit: Although extrusion technology provides high precision, if the heat sink design does not perfectly match the electronic component, it may result in poor heat dissipation or even overheating. Therefore, when designing, ensure that the size and shape of the heat sink can perfectly fit the electronic component to be cooled.
Poor Airflow: If the electronic device is operating in an environment with poor airflow or the housing of the device is too tight, the heat sink may not be able to dissipate heat effectively. At this time, it is necessary to ensure that the device is well ventilated to optimize the heat dissipation effect.
Corrosion: Although aluminum itself has good corrosion resistance, corrosion may occur on the surface of the heat sink in harsh environments such as high humidity or salt spray. This problem can be alleviated by using surface treatments such as anodizing or spraying.
Mechanical Damage: Extruded heat sinks, especially those with sharp fins, are susceptible to mechanical damage during handling or installation. Careful handling is required during production, transportation, and installation to avoid physical damage that affects heat dissipation performance.
Cost-effectiveness issue: Although extruded heat sinks are relatively low-cost compared to other types of heat sinks, initial tooling and production costs may be high if custom designs are required. However, ordering in large quantities can help reduce the cost of individual products.
Extruded heat sinks play a vital role in modern electronic systems, helping to manage thermal performance and ensure long life and reliability of equipment. KingKa is able to provide highly customized solutions and manufacture high-precision heat sinks that meet specific application needs.
Kingka Tech Industrial Limited
We specialize in precision CNC machining and our products are widely used in telecommunication industry, aerospace, automotive, industrial control, power electronics, medical instruments, security electronics, LED lighting and multimedia consumption.
Address:
Da Long New Village, Xie Gang Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China 523598
Email:
Tel:
+86 137 1244 4018